A Short Introduction to Algebraic Taxonomy on Genes Regions. II
Robersy Sanchez
Department of Biology. Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802rus547@psu.edu
28 December 2024
Source:vignettes/automorphism_and_decision_tree_II.Rmd
automorphism_and_decision_tree_II.RmdAbstract
A fast introduction into the analysis of DNA mutational events by means of automorphisms between two DNA sequences algebraically represented as Abelian finite group. In the current case we propose expressing of the effect of mutational events in terms of distance between codons in the framework set in reference (1). The decision tree is build based on Chi-squared Automated Interaction Detection (CHAID) algorithm.
Overview
This is part II of the tutorial A Short Introduction to Algebraic Taxonomy on Genes Regions
Decision tree
Although the analysis will be accomplish in a dataset with 41 DNA sequences, mostly humans, still the information from other species is poor. So, the conclusion retrieved from the analysis most be taken cautiously, and these are only for illustrative purpose on the application of the theory.
If all the required libraries all installed, then we proceed to load the libraries
library(GenomAutomorphism)
#> Error in get(paste0(generic, ".", class), envir = get_method_env()) :
#> object 'type_sum.accel' not found
library(Biostrings)
library(party)
library(partykit)
library(data.table)
library(ggplot2)
library(ggparty)
library(dplyr)
library(CHAID)The dataset carrying 41 aligned DNA sequences of BRCA1 genes from primates is provided with the package.
data(brca1_aln2, package = "GenomAutomorphism")
brca1_aln2
#> DNAMultipleAlignment with 41 rows and 2283 columns
#> aln names
#> [1] ATGGATTTATCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA NM_007298.3:20-22...
#> [2] ATGGATTTATCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA U64805.1:1-2280_H...
#> [3] ATGGATTTCTCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA NM_007298.3:20-22...
#> [4] ATGGATTTGTCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA NM_007298.3:20-22...
#> [5] ATGGATTTTTCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA NM_007298.3:20-22...
#> [6] ATGGATTTTTCTGCTCTTCGGGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA NM_007298.3:20-22...
#> [7] ATGGATTTTTCTGCTCTTCGCTTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA NM_007298.3:20-22...
#> [8] ATGGATTTTTCTGCTCTTCGCCTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA NM_007298.3:20-22...
#> [9] ATGGATTTTTCTGCTCTTCGCATTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA NM_007298.3:20-22...
#> ... ...
#> [33] ATGGATTTATCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCTCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_034941185.1:24...
#> [34] ATGGATTTATCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCTCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_034941182.1:25...
#> [35] ATGGATTTATCTGCTGTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGATACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_032163757.1:14...
#> [36] ATGGATTTATCTGCTGTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGATACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_032163756.1:14...
#> [37] ATGGATTTATCTGCTGTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGATACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_032163758.1:13...
#> [38] ATGGATTTATCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACGCCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_030923119.1:18...
#> [39] ATGGATTTATCTGCTCTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACGCCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_030923118.1:18...
#> [40] ATGGATTTACCTGCTGTTCGCGTTGAAGAAGTACAAAATGTCATT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCCCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_025363316.1:14...
#> [41] ATGGATTTATCTGCTGTTCGTGTTGAAGAAGTGCAAAATGTCCTT...CTGGACACCTACCTGATACCCCAGATCCCTCACAGCCACTACTGA XM_039475995.1:49...The sample names
strtrim(names(brca1_aln2@unmasked), 100)
#> [1] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_variant_4_mRNA"
#> [2] "U64805.1:1-2280_Homo_sapiens_Brca1-delta11b_(Brca1)_mRNA_complete_cds"
#> [3] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_9A-C_L3F_rs780157871"
#> [4] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_9A-G_rs780157871"
#> [5] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_9A-T_L3F_rs780157871"
#> [6] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_21C-G_rs149402012"
#> [7] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_22G-T_V8F_rs528902306"
#> [8] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_22G-C_V8L_rs528902306"
#> [9] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_22G-A_V8I_rs528902306"
#> [10] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_75C-T_rs80356839"
#> [11] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_999T-A_rs1060915"
#> [12] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_985A-C_I329L_rs80357157"
#> [13] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_1014C-A_D338E_rs1057523168"
#> [14] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_1134A-C_rs1555582589."
#> [15] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_1327G-T_D443Y_rs28897691"
#> [16] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_1327G-C_D443H_rs28897691"
#> [17] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_1327G-A_D443N_rs28897691"
#> [18] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_1348T-A_L450M_rs80357431"
#> [19] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_2100T-C_rs2050995166"
#> [20] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_2102T-G_V701G_rs80356920"
#> [21] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_2102T-C_V701A_rs80356920"
#> [22] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_2102T-A_V701D_rs80356920"
#> [23] "NM_007298.3:20-2299_Homo_sapiens_BRCA1_transcript_variant_4_mRNA_305C-G_A102G_rs80357190"
#> [24] "XM_031011560.1:233-2515_PREDICTED:_Gorilla_gorilla_gorilla_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_trans"
#> [25] "XM_031011561.1:233-2512_PREDICTED:_Gorilla_gorilla_gorilla_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_trans"
#> [26] "XM_031011562.1:163-2442_PREDICTED:_Gorilla_gorilla_gorilla_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_trans"
#> [27] "XM_009432101.3:276-2555_PREDICTED:_Pan_troglodytes_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_va"
#> [28] "XM_009432104.3:371-2650_PREDICTED:_Pan_troglodytes_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_va"
#> [29] "XM_016930487.2:371-2650_PREDICTED:_Pan_troglodytes_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_va"
#> [30] "XM_009432099.3:371-2653_PREDICTED:_Pan_troglodytes_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_va"
#> [31] "XM_034941183.1:254-2533_PREDICTED:_Pan_paniscus_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_varia"
#> [32] "XM_034941184.1:254-2533_PREDICTED:_Pan_paniscus_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_varia"
#> [33] "XM_034941185.1:248-2527_PREDICTED:_Pan_paniscus_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_varia"
#> [34] "XM_034941182.1:254-2536_PREDICTED:_Pan_paniscus_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_varia"
#> [35] "XM_032163757.1:145-2418_PREDICTED:_Hylobates_moloch_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_v"
#> [36] "XM_032163756.1:145-2421_PREDICTED:_Hylobates_moloch_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_v"
#> [37] "XM_032163758.1:139-2412_PREDICTED:_Hylobates_moloch_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcript_v"
#> [38] "XM_030923119.1:184-2463_PREDICTED:_Rhinopithecus_roxellana_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_trans"
#> [39] "XM_030923118.1:183-2465_PREDICTED:_Rhinopithecus_roxellana_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_trans"
#> [40] "XM_025363316.1:147-2426_PREDICTED:_Theropithecus_gelada_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1)_transcri"
#> [41] "XM_039475995.1:49-2328_PREDICTED:_Saimiri_boliviensis_boliviensis_BRCA1_DNA_repair_associated_(BRCA1"The automorphisms can be computed as before. For the sake of saving time object brca1_autm2 is included with package
## Do not run it. This is included with package
nams <- c(paste0("human_1.", 0:21),"human_2","gorilla_1","gorilla_2","gorilla_3",
"chimpanzee_1","chimpanzee_2","chimpanzee_3","chimpanzee_4",
"bonobos_1","bonobos_2","bonobos_3","bonobos_4","silvery_gibbon_1",
"silvery_gibbon_1","silvery_gibbon_3","golden_monkey_1",
"golden_monkey_2","gelada_baboon","bolivian_monkey")
brca1_autm2 <- automorphisms(
seqs = brca1_aln2,
group = "Z64",
cube = c("ACGT", "TGCA"),
cube_alt = c("CATG", "GTAC"),
nms = nams,
verbose = FALSE)Object brca1_autm2 can be load typing:
data(brca1_autm2, package = "GenomAutomorphism")
brca1_autm2
#> AutomorphismList object of length: 820
#> names(820): human_1.0.human_1.1 human_1.0.human_1.2 human_1.0.human_1.3 ... golden_monkey_2.gelada_baboon golden_monkey_2.bolivian_monkey gelada_baboon.bolivian_monkey
#> -------
#> Automorphism object with 761 ranges and 8 metadata columns:
#> seqnames ranges strand | seq1 seq2 aa1 aa2 coord1 coord2 autm
#> <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <character> <character> <character> <character> <numeric> <numeric> <numeric>
#> [1] 1 1 + | ATG ATG M M 50 50 1
#> [2] 1 2 + | GAT GAT D D 11 11 1
#> [3] 1 3 + | TTA TTA L L 60 60 1
#> [4] 1 4 + | TCT TCT S S 31 31 1
#> [5] 1 5 + | GCT GCT A A 27 27 1
#> ... ... ... ... . ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
#> [757] 1 757 + | CAC CAC H H 5 5 1
#> [758] 1 758 + | AGC AGC S S 33 33 1
#> [759] 1 759 + | CAC CAC H H 5 5 1
#> [760] 1 760 + | TAC TAC Y Y 13 13 1
#> [761] 1 761 + | TGA TGA * * 44 44 1
#> cube
#> <character>
#> [1] ACGT
#> [2] ACGT
#> [3] ACGT
#> [4] ACGT
#> [5] ACGT
#> ... ...
#> [757] ACGT
#> [758] ACGT
#> [759] ACGT
#> [760] ACGT
#> [761] ACGT
#> -------
#> seqinfo: 1 sequence from an unspecified genome; no seqlengths
#> ...
#> <819 more DFrame element(s)>
#> Two slots: 'DataList' & 'SeqRanges'
#> -------As before, we are interested on mutational events in respect to human (as reference).
nams <- names(brca1_autm2)
idx1 <- grep("human_1.", nams)
idx2 <- grep("human_2.", nams)
idx <- union(idx1, idx2)
h_brca1_autm <- unlist(brca1_autm2[ idx ])
h_brca1_autm = h_brca1_autm[ which(h_brca1_autm$autm != 1) ]
h_brca1_autm
#> Automorphism object with 16542 ranges and 8 metadata columns:
#> seqnames ranges strand | seq1 seq2 aa1 aa2 coord1
#> <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <character> <character> <character> <character> <numeric>
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 1 239 + | CAT CGT H R 7
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 1 253 + | GCA GTA A V 24
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 1 323 + | TCT CCT S P 31
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 1 333 + | TCT TCC S S 31
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 1 350 + | --- --- - - NA
#> ... ... ... ... . ... ... ... ... ...
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 1 716 + | AAT AGT N S 3
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 1 726 + | GAG GAA E E 10
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 1 730 + | GTG GTA V V 58
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 1 731 + | ACC ACT T T 17
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 1 756 + | CCC CCT P P 21
#> coord2 autm cube
#> <numeric> <numeric> <character>
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 39 33 ACGT
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 56 21 ACGT
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 23 9 ACGT
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 29 3 ACGT
#> human_1.0.human_1.1 NA -1 Gaps
#> ... ... ... ...
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 35 33 ACGT
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 8 52 ACGT
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 56 12 ACGT
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 19 35 ACGT
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 23 59 ACGT
#> -------
#> seqinfo: 1 sequence from an unspecified genome; no seqlengthsAutmorphism Grouping by Coefficient
The automorphism distribution by cubes can be summarized in the bar-plot graphic.
Object autby_coef carried all the pairwise comparisons, while it will be enough to use data from a single species as reference, e.g., humans.
First the data must be reordered into a object:
h_autby_coef <- automorphism_bycoef(x = h_brca1_autm)
h_autby_coef
#> AutomorphismByCoef object with 16515 ranges and 7 metadata columns:
#> seqnames ranges strand | seq1 seq2 aa1 aa2 autm
#> <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> | <character> <character> <character> <character> <numeric>
#> human_1.0.human_1.2 1 3 + | TTA TTC L F 22
#> human_1.0.human_1.3 1 3 + | TTA TTG L L 43
#> human_1.0.human_1.4 1 3 + | TTA TTT L F 0
#> human_1.0.human_1.5 1 3 + | TTA TTT L F 0
#> human_1.0.human_1.6 1 3 + | TTA TTT L F 0
#> ... ... ... ... . ... ... ... ... ...
#> human_1.18.bolivian_monkey 1 756 + | CCC CCT P P 59
#> human_1.19.bolivian_monkey 1 756 + | CCC CCT P P 59
#> human_1.20.bolivian_monkey 1 756 + | CCC CCT P P 59
#> human_1.21.bolivian_monkey 1 756 + | CCC CCT P P 59
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey 1 756 + | CCC CCT P P 59
#> mut_type cube
#> <character> <character>
#> human_1.0.human_1.2 HHM TGCA
#> human_1.0.human_1.3 HHR TGCA
#> human_1.0.human_1.4 HHW Trnl
#> human_1.0.human_1.5 HHW Trnl
#> human_1.0.human_1.6 HHW Trnl
#> ... ... ...
#> human_1.18.bolivian_monkey HHY ACGT
#> human_1.19.bolivian_monkey HHY ACGT
#> human_1.20.bolivian_monkey HHY ACGT
#> human_1.21.bolivian_monkey HHY ACGT
#> human_2.bolivian_monkey HHY ACGT
#> -------
#> seqinfo: 1 sequence from an unspecified genome; no seqlengthsThe counts by type of mutations
table(h_autby_coef$mut_type)
#>
#> --- HHH HHK HHM HHR HHS HHW HHY HKH HMH HMR HRH HRR HRW HRY HSH HWH HYH HYS KHH KKH KWH KYH MHH
#> 575 391 290 447 2050 270 769 2358 126 829 253 1648 69 3 46 271 195 626 46 179 3 3 3 573
#> RHH RKH RMH RWH RYH SHH SHM WHH WHK YHH YRH YRY
#> 2469 1 46 1 1 874 1 229 23 755 69 23Simplifying species names
nams <- names(h_autby_coef)
nams <- sub("human[_][1-2][.]", "", nams)
nams <- sub("[_][1-6]", "", nams)
nams <- sub("[0123456789]*[.]", "", nams)
nams <- sub("[.][0123456789]*", "", nams)
dt <- data.frame(h_autby_coef, species = nams)
dt <- data.frame(dt, species = nams)
dt <- dt[, c("start", "autm", "species", "mut_type", "aa1", "aa2", "cube")]
DataFrame(dt)
#> DataFrame with 16515 rows and 7 columns
#> start autm species mut_type aa1 aa2 cube
#> <integer> <numeric> <character> <character> <character> <character> <character>
#> 1 3 22 human HHM L F TGCA
#> 2 3 43 human HHR L L TGCA
#> 3 3 0 human HHW L F Trnl
#> 4 3 0 human HHW L F Trnl
#> 5 3 0 human HHW L F Trnl
#> ... ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
#> 16511 756 59 bolivian_monkey HHY P P ACGT
#> 16512 756 59 bolivian_monkey HHY P P ACGT
#> 16513 756 59 bolivian_monkey HHY P P ACGT
#> 16514 756 59 bolivian_monkey HHY P P ACGT
#> 16515 756 59 bolivian_monkey HHY P P ACGTNominal variables are transformed into
dt$start <- as.numeric(dt$start)
dt$autm <- as.numeric(dt$autm)
dt$cube <- as.factor(dt$cube)
dt$species <- as.factor(dt$species)
dt$mut_type <- as.factor(dt$mut_type)CHAID using aminoacid/codon distance
In this analysis a new variable has been include, which derives from the estimation of the distance between aminoacids, estimated as suggested in reference (1). The mutational effect is measured in terms of the average of two aminoacid distance functions, which are based on the codon distance.
interval <- function(x, a, b) {
x >= a & x <= b
}
datos = dt
datos$mut_cost <- round((aminoacid_dist(aa1 = h_autby_coef, group = "Z5",
cube = "TCGA" , num.cores = 20) +
aminoacid_dist(aa1 = h_autby_coef,
weight = c(0.3, 0.9, 0.08), group = "Z5",
cube = "TCGA" , num.cores = 20))/2, 2)
hist(datos$mut_cost,10)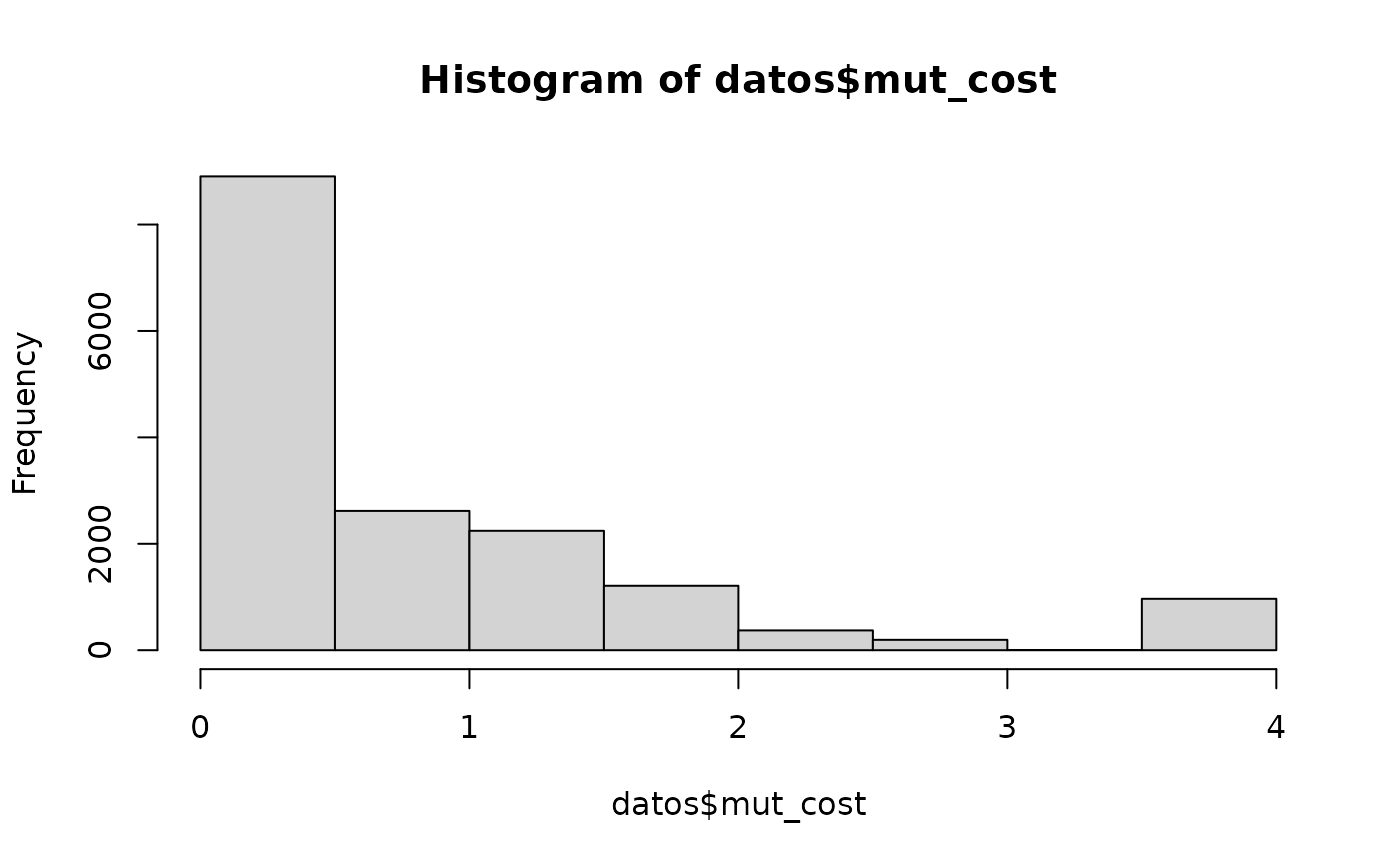
datos$mut_cost[ is.na(datos$mut_cost) ] <- -10
datos$autms <- case_when(datos$autm < 16 ~ 'A1',
interval(datos$autm, 16, 31) ~ 'A2',
interval(datos$autm, 32, 47) ~ 'A3',
datos$autm > 47 ~ 'A4')
datos$autms <- as.factor(datos$autms)
datos$mut_type <- as.character(datos$mut_type)
datos$mut_type <- as.factor(datos$mut_type)
datos$regions <- case_when(datos$start < 102 ~ 'R0',
interval(datos$start, 103, 229) ~ 'R0.',
interval(datos$start, 230, 270) ~ 'R1',
interval(datos$start, 271, 305) ~ 'R2',
interval(datos$start, 306, 338) ~ 'R3',
interval(datos$start, 339, 533) ~ 'R4',
interval(datos$start, 534, 570) ~ 'R5',
interval(datos$start, 571, 653) ~ 'R6',
interval(datos$start, 654, 709) ~ 'R7',
datos$start > 709 ~ 'R8')
datos$regions <- as.factor(datos$regions)
datos$autm <- as.factor(datos$autm)
datos$species <- as.factor(datos$species)
datos$start <- as.factor(datos$start)
datos$cube <- as.factor(datos$cube)
datos$mut_cost <- as.factor(datos$mut_cost)
datos <- datos[, c( "autms", "regions", "mut_type", "cube", "mut_cost", "species")]
DataFrame(datos)
#> DataFrame with 16515 rows and 6 columns
#> autms regions mut_type cube mut_cost species
#> <factor> <factor> <factor> <factor> <factor> <factor>
#> 1 A2 R0 HHM TGCA 0.26 human
#> 2 A3 R0 HHR TGCA 0.22 human
#> 3 A1 R0 HHW Trnl 0.26 human
#> 4 A1 R0 HHW Trnl 0.26 human
#> 5 A1 R0 HHW Trnl 0.26 human
#> ... ... ... ... ... ... ...
#> 16511 A4 R8 HHY ACGT 0.1 bolivian_monkey
#> 16512 A4 R8 HHY ACGT 0.1 bolivian_monkey
#> 16513 A4 R8 HHY ACGT 0.1 bolivian_monkey
#> 16514 A4 R8 HHY ACGT 0.1 bolivian_monkey
#> 16515 A4 R8 HHY ACGT 0.1 bolivian_monkeyThe histogram shows an expected result for a variable measuring the mutational effect: the frequency of mutational events must (exponentially) decrease with the magnitude of the mutational effect.
A classification tree is estimated with CHAID algorithm:
ctrl <- chaid_control(minsplit = 500, minprob = 0.9, alpha2 = 0.01, alpha4 = 0.01)
chaid_res <- chaid(species ~ autms + regions + mut_type + cube + mut_cost,
data = datos, control = ctrl)
chaid_res
#>
#> Model formula:
#> species ~ autms + regions + mut_type + cube + mut_cost
#>
#> Fitted party:
#> [1] root
#> | [2] mut_cost in 0.06
#> | | [3] regions in R0, R5: bolivian_monkey (n = 220, err = 68.6%)
#> | | [4] regions in R0.: bolivian_monkey (n = 253, err = 45.5%)
#> | | [5] regions in R1: golden_monkey (n = 230, err = 60.0%)
#> | | [6] regions in R2: bolivian_monkey (n = 115, err = 40.0%)
#> | | [7] regions in R3: gelada_baboon (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [8] regions in R4
#> | | | [9] autms in A1, A3: golden_monkey (n = 322, err = 57.1%)
#> | | | [10] autms in A2: golden_monkey (n = 276, err = 66.7%)
#> | | | [11] autms in A4: gorilla (n = 92, err = 25.0%)
#> | | [12] regions in R6: silvery_gibbon (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [13] regions in R7: silvery_gibbon (n = 187, err = 61.5%)
#> | | [14] regions in R8: silvery_gibbon (n = 89, err = 25.8%)
#> | [15] mut_cost in 0.1
#> | | [16] regions in R0, R2: golden_monkey (n = 243, err = 62.1%)
#> | | [17] regions in R0.: bonobos (n = 322, err = 71.4%)
#> | | [18] regions in R1: gorilla (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [19] regions in R3: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [20] regions in R4: silvery_gibbon (n = 407, err = 65.4%)
#> | | [21] regions in R5, R7: bolivian_monkey (n = 135, err = 31.1%)
#> | | [22] regions in R6: bolivian_monkey (n = 138, err = 66.7%)
#> | | [23] regions in R8: bonobos (n = 319, err = 71.2%)
#> | [24] mut_cost in 0.12, 0.35
#> | | [25] regions in R0, R6, R7, R8: silvery_gibbon (n = 223, err = 67.7%)
#> | | [26] regions in R0.: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [27] regions in R1, R5: silvery_gibbon (n = 135, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [28] regions in R2: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [29] regions in R3: human (n = 40, err = 45.0%)
#> | | [30] regions in R4: bolivian_monkey (n = 115, err = 60.0%)
#> | [31] mut_cost in 0.22
#> | | [32] regions in R0, R1, R3, R8: golden_monkey (n = 164, err = 70.7%)
#> | | [33] regions in R0.: silvery_gibbon (n = 138, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [34] regions in R2: golden_monkey (n = 138, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [35] regions in R4: bolivian_monkey (n = 161, err = 42.9%)
#> | | [36] regions in R5: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [37] regions in R6: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [38] regions in R7: gelada_baboon (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [39] mut_cost in 0.26
#> | | [40] autms in A1, A2: human (n = 424, err = 71.5%)
#> | | [41] autms in A3: silvery_gibbon (n = 93, err = 22.6%)
#> | | [42] autms in A4: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 0.0%)
#> | [43] mut_cost in 0.28, 1.23
#> | | [44] regions in R0, R3, R6, R7, R8: golden_monkey (n = 276, err = 66.7%)
#> | | [45] regions in R0.: bonobos (n = 115, err = 20.0%)
#> | | [46] regions in R1: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [47] regions in R2: bonobos (n = 414, err = 77.8%)
#> | | [48] regions in R4
#> | | | [49] autms in A1: golden_monkey (n = 162, err = 43.2%)
#> | | | [50] autms in A2: human (n = 42, err = 71.4%)
#> | | | [51] autms in A3: bonobos (n = 488, err = 81.1%)
#> | | | [52] autms in A4: human (n = 14, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [53] regions in R5: golden_monkey (n = 161, err = 42.9%)
#> | [54] mut_cost in 0.31: golden_monkey (n = 184, err = 50.0%)
#> | [55] mut_cost in 0.32
#> | | [56] regions in R0, R0., R3: bonobos (n = 111, err = 20.7%)
#> | | [57] regions in R1: chimpanzee (n = 326, err = 71.8%)
#> | | [58] regions in R2: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [59] regions in R4: silvery_gibbon (n = 184, err = 62.5%)
#> | | [60] regions in R5, R7: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [61] regions in R6: gorilla (n = 138, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [62] regions in R8: golden_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | [63] mut_cost in 0.33: golden_monkey (n = 448, err = 58.5%)
#> | [64] mut_cost in 0.41: silvery_gibbon (n = 150, err = 54.0%)
#> | [65] mut_cost in 0.47, 0.81: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | [66] mut_cost in 0.53: gorilla (n = 338, err = 78.7%)
#> | [67] mut_cost in 0.58, 0.78, 1.02: golden_monkey (n = 454, err = 69.6%)
#> | [68] mut_cost in 0.63: golden_monkey (n = 109, err = 56.0%)
#> | [69] mut_cost in 0.67: golden_monkey (n = 109, err = 56.0%)
#> | [70] mut_cost in 0.73, 0.82, 1.52, 2.48: silvery_gibbon (n = 300, err = 53.0%)
#> | [71] mut_cost in 0.89: bolivian_monkey (n = 184, err = 50.0%)
#> | [72] mut_cost in 0.94, 1.03: golden_monkey (n = 276, err = 50.0%)
#> | [73] mut_cost in 0.98: bolivian_monkey (n = 207, err = 66.7%)
#> | [74] mut_cost in 0.99
#> | | [75] regions in R0, R0., R6, R8: bonobos (n = 414, err = 77.8%)
#> | | [76] regions in R1: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [77] regions in R2: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [78] regions in R3: human (n = 79, err = 45.6%)
#> | | [79] regions in R4, R7: golden_monkey (n = 299, err = 53.8%)
#> | | [80] regions in R5: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [81] mut_cost in 1.01: golden_monkey (n = 207, err = 55.6%)
#> | [82] mut_cost in 1.11, 1.28: bolivian_monkey (n = 93, err = 49.5%)
#> | [83] mut_cost in 1.12, 1.89, 2.88: gorilla (n = 224, err = 67.9%)
#> | [84] mut_cost in 1.18: bonobos (n = 256, err = 64.1%)
#> | [85] mut_cost in 1.19: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [86] mut_cost in 1.21
#> | | [87] regions in R0, R0., R1, R2, R3, R5, R6, R8: golden_monkey (n = 129, err = 62.8%)
#> | | [88] regions in R4: bonobos (n = 414, err = 77.8%)
#> | | [89] regions in R7: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [90] mut_cost in 1.34: bonobos (n = 437, err = 78.9%)
#> | [91] mut_cost in 1.36: gorilla (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | [92] mut_cost in 1.58, 3.38: silvery_gibbon (n = 95, err = 27.4%)
#> | [93] mut_cost in 1.98
#> | | [94] regions in R0, R0., R2, R3, R5, R8: bonobos (n = 460, err = 80.0%)
#> | | [95] regions in R1: silvery_gibbon (n = 161, err = 57.1%)
#> | | [96] regions in R4: silvery_gibbon (n = 368, err = 43.8%)
#> | | [97] regions in R6: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [98] regions in R7: human (n = 35, err = 40.0%)
#> | [99] mut_cost in 2.12, 3.17: golden_monkey (n = 70, err = 34.3%)
#> | [100] mut_cost in 2.14: bolivian_monkey (n = 230, err = 70.0%)
#> | [101] mut_cost in 2.22, 2.23: bolivian_monkey (n = 70, err = 32.9%)
#> | [102] mut_cost in 2.92: golden_monkey (n = 80, err = 42.5%)
#> | [103] mut_cost in 2.99: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [104] mut_cost in 4
#> | | [105] mut_type in ---, HHK, HHM, HHR, HHS, HHW, HHY, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRH, YRY
#> | | | [106] regions in R0, R0., R1, R3, R5, R6, R7, R8: silvery_gibbon (n = 253, err = 36.4%)
#> | | | [107] regions in R2: bonobos (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [108] regions in R4: bonobos (n = 299, err = 76.9%)
#> | | [109] mut_type in HHH: human (n = 391, err = 35.3%)
#>
#> Number of inner nodes: 15
#> Number of terminal nodes: 94Plotting the CHAID tree (II)
Next, the data must be prepared for plotting the tree with ggparty:
## Updating CHAID decision tree
dp <- data_party(chaid_res)
dat <- dp[, c("autms", "regions", "mut_type", "mut_cost")]
dat$species <- dp[, "(response)"]
chaid_tree <- party(node = node_party(chaid_res),
data = dat,
fitted = dp[, c("(fitted)", "(response)")],
names = names(chaid_res))
## Extract p-values
pvals <- unlist(nodeapply(chaid_tree, ids = nodeids(chaid_tree), function(n) {
pvals <- info_node(n)$adjpvals
pvals < pvals[ which.min(pvals) ]
return(pvals)
}))
pvals <- pvals[ pvals < 0.05 ]
## Counts of event per spciees on each node
node.freq <- sapply(seq_along(chaid_tree), function(id) {
y <- data_party(chaid_tree, id = id)
y <- y[[ "(response)" ]]
table(y)
})
## total counts on each
node.size = colSums(node.freq)Plotting the tree with ggparty (font size adjusted for html output)
ggparty(chaid_tree, horizontal = TRUE) +
geom_edge(aes(color = id, size = node.size[id]/300), show.legend = FALSE) +
geom_edge_label(size = 12, colour = "red",
fontface = "bold",
shift = 0.64,
nudge_x = -0.01,
max_length = 10,
splitlevels = 1:4) +
geom_node_label(line_list = list(aes(label = paste0("Node ", id, ": ", splitvar)),
aes(label = paste0("N=", node.size[id], ", p",
ifelse(pvals < .001, "<.001",
paste0("=", round(pvals, 3)))),
size = 30)),
line_gpar = list(list(size = 30),
list(size = 30)),
ids = "inner", fontface = "bold", size = 30) +
geom_node_info() +
geom_node_label(aes(label = paste0("N = ", node.size),
fontface = "bold"),
ids = "terminal", nudge_y = -0.0, nudge_x = 0.01, size = 12) +
geom_node_plot(gglist = list(
geom_bar(aes(x = "", fill = species), size = 0.7, width = 0.9,
position = position_fill(), color = "black"),
theme_minimal(base_family = "arial", base_size = 20),
theme(legend.key.size = unit(2, "cm"),
legend.key.width = unit(3.5, 'cm'),
legend.text = element_text(size = 50),
legend.title = element_text(size = 52),
text = element_text(size = 44)),
coord_flip(),
scale_fill_manual(values = c("gray50","gray55","gray60",
"gray70","gray80","gray85",
"dodgerblue","gray95")),
xlab(""),
ylab("Probability"),
geom_text(aes(x = "", group = species,
label = stat(count)),
stat = "count", position = position_fill(),
vjust = 0.6, hjust = 1.5, size = 14)),
shared_axis_labels = TRUE, size = 1.4)
It is important to observe that, as shown in reference (1), that the optimal weights applied to compute the aminoacid distances can be estimated for each gene or genomic region via genetic algorithm. The optimization takes place by simulating the mutational process in the corresponding gene/region population.
Stochastic-deterministic logical rules
Since only one mutational event human-to-human in region R1 from class A3 is reported in the right side of the tree, with high probability only non-humans hold the following rule:
rule <- (dat$mut_cost == 1.34 )
table(as.character(dat[rule,]$species))
#>
#> bolivian_monkey bonobos chimpanzee gelada_baboon golden_monkey silvery_gibbon
#> 46 92 92 46 92 69Only humans-to-human mutations hold the following rule:
rule <- (dat$mut_cost == 0.28 & dat$regions == "R4" & dat$autm == "A4")
table(as.character(dat[ rule, ]$species))
#>
#> human
#> 14Only gorilla hold the following rule
rule <- (dat$mut_cost == 1.36 )
table(as.character(dat[rule,]$species))
#>
#> gorilla
#> 69Only Bolivian monkey holds:
rule <- ((dat$mut_cost == 0.12 | dat$mut_cost == 0.35) & (dat$regions == "R1" | dat$regions == "R5"))
table(as.character(dat[rule,]$species))
#>
#> silvery_gibbon
#> 135CHAID with different model
ctrl <- chaid_control(minsplit = 200, minprob = 0.9, alpha2 = 0.01, alpha4 = 0.05)
chaid_res <- chaid(species ~ autms + regions + mut_type + mut_cost,
data = datos, control = ctrl)
chaid_res
#>
#> Model formula:
#> species ~ autms + regions + mut_type + mut_cost
#>
#> Fitted party:
#> [1] root
#> | [2] mut_cost in 0.06
#> | | [3] regions in R0, R5
#> | | | [4] autms in A1: silvery_gibbon (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [5] autms in A2: gorilla (n = 92, err = 25.0%)
#> | | | [6] autms in A3: human (n = 13, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [7] autms in A4: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [8] regions in R0.
#> | | | [9] autms in A1, A4: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [10] autms in A2: bolivian_monkey (n = 138, err = 50.0%)
#> | | | [11] autms in A3: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [12] regions in R1
#> | | | [13] autms in A1, A4: golden_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [14] autms in A2: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | | [15] autms in A3: silvery_gibbon (n = 115, err = 40.0%)
#> | | [16] regions in R2: bolivian_monkey (n = 115, err = 40.0%)
#> | | [17] regions in R3: gelada_baboon (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [18] regions in R4
#> | | | [19] autms in A1, A3: golden_monkey (n = 322, err = 57.1%)
#> | | | [20] autms in A2
#> | | | | [21] mut_type in ---, HHH, HHK, HHM, HHR, HHS, HHW, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRH, YRY: golden_monkey (n = 253, err = 63.6%)
#> | | | | [22] mut_type in HHY: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [23] autms in A4: gorilla (n = 92, err = 25.0%)
#> | | [24] regions in R6: silvery_gibbon (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [25] regions in R7: silvery_gibbon (n = 187, err = 61.5%)
#> | | [26] regions in R8: silvery_gibbon (n = 89, err = 25.8%)
#> | [27] mut_cost in 0.1
#> | | [28] regions in R0, R2
#> | | | [29] autms in A1, A3: golden_monkey (n = 184, err = 50.0%)
#> | | | [30] autms in A2: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [31] autms in A4: human (n = 36, err = 38.9%)
#> | | [32] regions in R0.
#> | | | [33] mut_type in ---, HHH, HHK, HHM, HHW, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRH, YRY: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [34] mut_type in HHR: gelada_baboon (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [35] mut_type in HHS: silvery_gibbon (n = 92, err = 25.0%)
#> | | | [36] mut_type in HHY: bonobos (n = 184, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [37] regions in R1: gorilla (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [38] regions in R3: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [39] regions in R4
#> | | | [40] mut_type in ---, HHH, HHK, HHS, HHY, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRH, YRY: gelada_baboon (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [41] mut_type in HHM: golden_monkey (n = 85, err = 43.5%)
#> | | | [42] mut_type in HHR: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | | [43] mut_type in HHW
#> | | | | [44] autms in A1, A2, A3: silvery_gibbon (n = 161, err = 57.1%)
#> | | | | [45] autms in A4: silvery_gibbon (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [46] regions in R5, R7: bolivian_monkey (n = 135, err = 31.1%)
#> | | [47] regions in R6: bolivian_monkey (n = 138, err = 66.7%)
#> | | [48] regions in R8
#> | | | [49] autms in A1, A2, A3: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [50] autms in A4: bonobos (n = 273, err = 66.3%)
#> | [51] mut_cost in 0.12, 0.35
#> | | [52] regions in R0, R6, R7, R8
#> | | | [53] mut_type in ---, HHH, HHK, HHM, HHR, HHW, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRH, YRY: silvery_gibbon (n = 162, err = 57.4%)
#> | | | [54] mut_type in HHS: human (n = 39, err = 43.6%)
#> | | | [55] mut_type in HHY: bolivian_monkey (n = 22, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [56] regions in R0.: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [57] regions in R1, R5: silvery_gibbon (n = 135, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [58] regions in R2: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [59] regions in R3: human (n = 40, err = 45.0%)
#> | | [60] regions in R4: bolivian_monkey (n = 115, err = 60.0%)
#> | [61] mut_cost in 0.22
#> | | [62] regions in R0, R1, R3, R8: golden_monkey (n = 164, err = 70.7%)
#> | | [63] regions in R0.: silvery_gibbon (n = 138, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [64] regions in R2: golden_monkey (n = 138, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [65] regions in R4: bolivian_monkey (n = 161, err = 42.9%)
#> | | [66] regions in R5: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [67] regions in R6: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [68] regions in R7: gelada_baboon (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [69] mut_cost in 0.26
#> | | [70] autms in A1, A2
#> | | | [71] regions in R0, R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8
#> | | | | [72] regions in R0, R0., R1, R2, R3, R5, R6, R7, R8
#> | | | | | [73] mut_type in ---, HHH, HHK, HHM, HHR, HHS, HHY, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRH, YRY: human (n = 17, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | | | [74] mut_type in HHW: human (n = 338, err = 69.2%)
#> | | | | [75] regions in R4: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [76] regions in R0.: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [77] autms in A3: silvery_gibbon (n = 93, err = 22.6%)
#> | | [78] autms in A4: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 0.0%)
#> | [79] mut_cost in 0.28, 1.23
#> | | [80] regions in R0, R3, R6, R7, R8
#> | | | [81] autms in A1, A2, A4: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [82] autms in A3
#> | | | | [83] mut_type in ---, HHH, HHK, HHM, HHR, HHS, HHW, HHY, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRY: silvery_gibbon (n = 161, err = 57.1%)
#> | | | | [84] mut_type in YRH: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [85] regions in R0.: bonobos (n = 115, err = 20.0%)
#> | | [86] regions in R1: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [87] regions in R2: bonobos (n = 414, err = 77.8%)
#> | | [88] regions in R4
#> | | | [89] autms in A1: golden_monkey (n = 162, err = 43.2%)
#> | | | [90] autms in A2: human (n = 42, err = 71.4%)
#> | | | [91] autms in A3: bonobos (n = 488, err = 81.1%)
#> | | | [92] autms in A4: human (n = 14, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [93] regions in R5: golden_monkey (n = 161, err = 42.9%)
#> | [94] mut_cost in 0.31: golden_monkey (n = 184, err = 50.0%)
#> | [95] mut_cost in 0.32
#> | | [96] regions in R0, R0., R3: bonobos (n = 111, err = 20.7%)
#> | | [97] regions in R1: chimpanzee (n = 326, err = 71.8%)
#> | | [98] regions in R2: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [99] regions in R4: silvery_gibbon (n = 184, err = 62.5%)
#> | | [100] regions in R5, R7: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [101] regions in R6: gorilla (n = 138, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [102] regions in R8: golden_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | [103] mut_cost in 0.33
#> | | [104] regions in R0, R4, R5, R8: human (n = 38, err = 47.4%)
#> | | [105] regions in R0., R2: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [106] regions in R1: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [107] regions in R3: silvery_gibbon (n = 137, err = 49.6%)
#> | | [108] regions in R6: golden_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [109] regions in R7: golden_monkey (n = 89, err = 48.3%)
#> | [110] mut_cost in 0.41: silvery_gibbon (n = 150, err = 54.0%)
#> | [111] mut_cost in 0.47, 0.81: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | [112] mut_cost in 0.53
#> | | [113] regions in R0, R0., R1, R2, R5, R6, R7, R8: gelada_baboon (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [114] regions in R3: silvery_gibbon (n = 92, err = 25.0%)
#> | | [115] regions in R4
#> | | | [116] autms in A1, A2, A4: bolivian_monkey (n = 150, err = 68.7%)
#> | | | [117] autms in A3: gorilla (n = 73, err = 5.5%)
#> | [118] mut_cost in 0.58, 0.78, 1.02
#> | | [119] regions in R0, R1, R2, R3, R5, R6, R8: human (n = 78, err = 46.2%)
#> | | [120] regions in R0.: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [121] regions in R4
#> | | | [122] autms in A1, A2: silvery_gibbon (n = 165, err = 58.2%)
#> | | | [123] autms in A3: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [124] autms in A4: golden_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [125] regions in R7: golden_monkey (n = 119, err = 66.4%)
#> | [126] mut_cost in 0.63: golden_monkey (n = 109, err = 56.0%)
#> | [127] mut_cost in 0.67: golden_monkey (n = 109, err = 56.0%)
#> | [128] mut_cost in 0.73, 0.82, 1.52, 2.48
#> | | [129] autms in A1: gelada_baboon (n = 28, err = 14.3%)
#> | | [130] autms in A2: silvery_gibbon (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [131] autms in A3: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [132] autms in A4: silvery_gibbon (n = 111, err = 35.1%)
#> | [133] mut_cost in 0.89: bolivian_monkey (n = 184, err = 50.0%)
#> | [134] mut_cost in 0.94, 1.03
#> | | [135] autms in A1, A2: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [136] autms in A3: golden_monkey (n = 184, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [137] autms in A4: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [138] mut_cost in 0.98
#> | | [139] regions in R0, R0., R1, R2, R3, R5, R6, R7, R8: silvery_gibbon (n = 161, err = 57.1%)
#> | | [140] regions in R4: bolivian_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | [141] mut_cost in 0.99
#> | | [142] regions in R0, R0., R6, R8: bonobos (n = 414, err = 77.8%)
#> | | [143] regions in R1: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [144] regions in R2: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [145] regions in R3: human (n = 79, err = 45.6%)
#> | | [146] regions in R4, R7
#> | | | [147] mut_type in ---, HHH, HHK, HHM, HHW, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRH, YRY: silvery_gibbon (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [148] mut_type in HHR: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [149] mut_type in HHS: golden_monkey (n = 46, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [150] mut_type in HHY: golden_monkey (n = 161, err = 42.9%)
#> | | [151] regions in R5: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [152] mut_cost in 1.01
#> | | [153] regions in R0, R0., R1, R2, R3, R5, R6, R7, R8: gorilla (n = 115, err = 40.0%)
#> | | [154] regions in R4: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 50.0%)
#> | [155] mut_cost in 1.11, 1.28: bolivian_monkey (n = 93, err = 49.5%)
#> | [156] mut_cost in 1.12, 1.89, 2.88
#> | | [157] regions in R0, R1, R2, R5, R6, R7, R8: golden_monkey (n = 92, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [158] regions in R0.: gorilla (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [159] regions in R3: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [160] regions in R4: human (n = 40, err = 45.0%)
#> | [161] mut_cost in 1.18: bonobos (n = 256, err = 64.1%)
#> | [162] mut_cost in 1.19: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [163] mut_cost in 1.21
#> | | [164] regions in R0, R0., R1, R2, R3, R5, R6, R8: golden_monkey (n = 129, err = 62.8%)
#> | | [165] regions in R4: bonobos (n = 414, err = 77.8%)
#> | | [166] regions in R7: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [167] mut_cost in 1.34
#> | | [168] regions in R0, R0., R1, R2, R3, R5, R8: golden_monkey (n = 138, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [169] regions in R4: bonobos (n = 184, err = 50.0%)
#> | | [170] regions in R6: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [171] regions in R7: silvery_gibbon (n = 92, err = 25.0%)
#> | [172] mut_cost in 1.36: gorilla (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | [173] mut_cost in 1.58, 3.38: silvery_gibbon (n = 95, err = 27.4%)
#> | [174] mut_cost in 1.98
#> | | [175] regions in R0, R0., R2, R3, R5, R8
#> | | | [176] autms in A1, A2, A3: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | | [177] autms in A4: bonobos (n = 391, err = 76.5%)
#> | | [178] regions in R1: silvery_gibbon (n = 161, err = 57.1%)
#> | | [179] regions in R4
#> | | | [180] autms in A1, A4: silvery_gibbon (n = 138, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [181] autms in A2: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | | [182] autms in A3: silvery_gibbon (n = 161, err = 57.1%)
#> | | [183] regions in R6: golden_monkey (n = 69, err = 33.3%)
#> | | [184] regions in R7: human (n = 35, err = 40.0%)
#> | [185] mut_cost in 2.12, 3.17: golden_monkey (n = 70, err = 34.3%)
#> | [186] mut_cost in 2.14
#> | | [187] regions in R0, R0., R1, R2, R3, R5, R6, R7: gorilla (n = 69, err = 0.0%)
#> | | [188] regions in R4: bolivian_monkey (n = 138, err = 66.7%)
#> | | [189] regions in R8: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [190] mut_cost in 2.22, 2.23: bolivian_monkey (n = 70, err = 32.9%)
#> | [191] mut_cost in 2.92: golden_monkey (n = 80, err = 42.5%)
#> | [192] mut_cost in 2.99: bolivian_monkey (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | [193] mut_cost in 4
#> | | [194] mut_type in ---, HHK, HHM, HHR, HHS, HHW, HHY, HKH, HMH, HMR, HRH, HRR, HRW, HRY, HSH, HWH, HYH, HYS, KHH, KKH, KWH, KYH, MHH, RHH, RKH, RMH, RWH, RYH, SHH, SHM, WHH, WHK, YHH, YRH, YRY
#> | | | [195] regions in R0, R0., R1, R3, R5, R6, R7, R8: silvery_gibbon (n = 253, err = 36.4%)
#> | | | [196] regions in R2: bonobos (n = 23, err = 0.0%)
#> | | | [197] regions in R4: bonobos (n = 299, err = 76.9%)
#> | | [198] mut_type in HHH: human (n = 391, err = 35.3%)
#>
#> Number of inner nodes: 45
#> Number of terminal nodes: 153Plotting the CHAID tree (III)
Next, the data must be prepared for plotting the tree with ggparty:
## Updating CHAID decision tree
dp <- data_party(chaid_res)
dat <- dp[, c("autms", "regions", "mut_type", "mut_cost")]
dat$species <- dp[, "(response)"]
chaid_tree <- party(node = node_party(chaid_res),
data = dat,
fitted = dp[, c("(fitted)", "(response)")],
names = names(chaid_res))
## Extract p-values
pvals <- unlist(nodeapply(chaid_tree, ids = nodeids(chaid_tree), function(n) {
pvals <- info_node(n)$adjpvals
pvals < pvals[ which.min(pvals) ]
return(pvals)
}))
pvals <- pvals[ pvals < 0.05 ]
## Counts of event per spciees on each node
node.freq <- sapply(seq_along(chaid_tree), function(id) {
y <- data_party(chaid_tree, id = id)
y <- y[[ "(response)" ]]
table(y)
})
## total counts on each
node.size = colSums(node.freq)Plotting the tree with ggparty (font size adjusted for html output)
ggparty(chaid_tree, horizontal = TRUE) +
geom_edge(aes(color = id, size = node.size[id]/300), show.legend = FALSE) +
geom_edge_label(size = 12, colour = "red",
fontface = "bold",
shift = 0.64,
nudge_x = -0.01,
max_length = 10,
splitlevels = 1:4) +
geom_node_label(line_list = list(aes(label = paste0("Node ", id, ": ", splitvar)),
aes(label = paste0("N=", node.size[id], ", p",
ifelse(pvals < .001, "<.001",
paste0("=", round(pvals, 3)))),
size = 30)),
line_gpar = list(list(size = 30),
list(size = 30)),
ids = "inner", fontface = "bold", size = 30) +
geom_node_info() +
geom_node_label(aes(label = paste0("N = ", node.size),
fontface = "bold"),
ids = "terminal", nudge_y = -0.0, nudge_x = 0.01, size = 12) +
geom_node_plot(gglist = list(
geom_bar(aes(x = "", fill = species), size = 0.7, width = 0.9,
position = position_fill(), color = "black"),
theme_minimal(base_family = "arial", base_size = 20),
theme(legend.key.size = unit(2, "cm"),
legend.key.width = unit(3.5, 'cm'),
legend.text = element_text(size = 50),
legend.title = element_text(size = 52),
text = element_text(size = 44)),
coord_flip(),
scale_fill_manual(values = c("gray50","gray55","gray60",
"gray70","gray80","gray85",
"dodgerblue","gray95")),
xlab(""),
ylab("Probability"),
geom_text(aes(x = "", group = species,
label = stat(count)),
stat = "count", position = position_fill(),
vjust = 0.6, hjust = 1.5, size = 14)),
shared_axis_labels = TRUE, size = 1.4)
rule <- (dat$mut_cost == 0.26 & (dat$autm == "A1" | dat$autm == "A2") & dat$regions != "R4" & dat$mut_type != "HHW")
table(as.character(dat[ rule, ]$species))
#>
#> human
#> 17
rule <- (dat$mut_cost == 0.99 & dat$mut_type == "HHS" & (dat$regions == "R7" | dat$regions == "R4"))
table(as.character(dat[ rule, ]$species))
#>
#> golden_monkey
#> 46References
Sanchez R. Evolutionary Analysis of DNA-Protein-Coding Regions Based on a Genetic Code Cube Metric. Curr Top Med Chem. 2014;14: 407–417. doi: 10.2174/1568026613666131204110022.
Robersy Sanchez, Jesús Barreto (2021) Genomic Abelian Finite Groups. doi: 10.1101/2021.06.01.446543.